Data Alteration Protection (DAP) Tool
Overview:
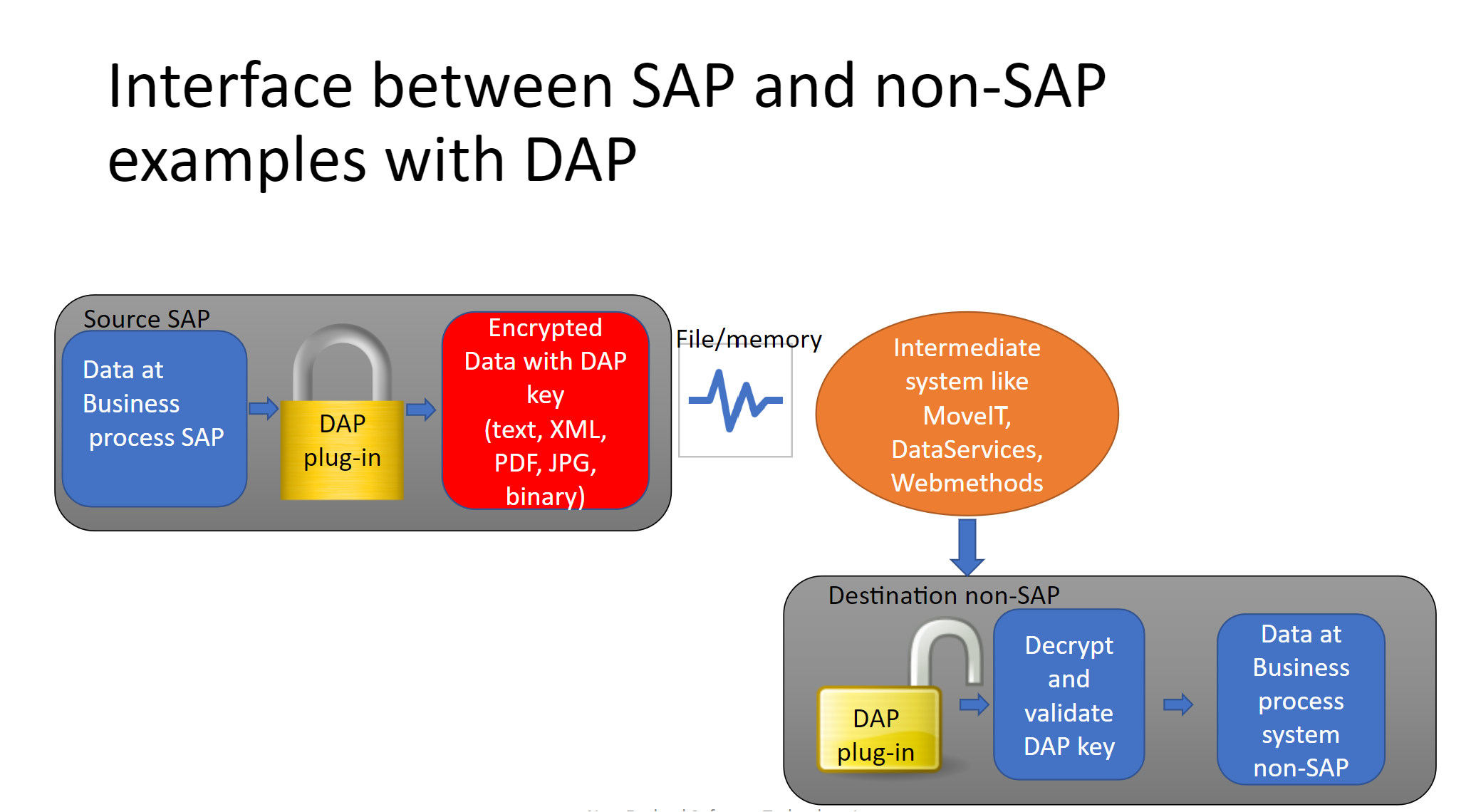
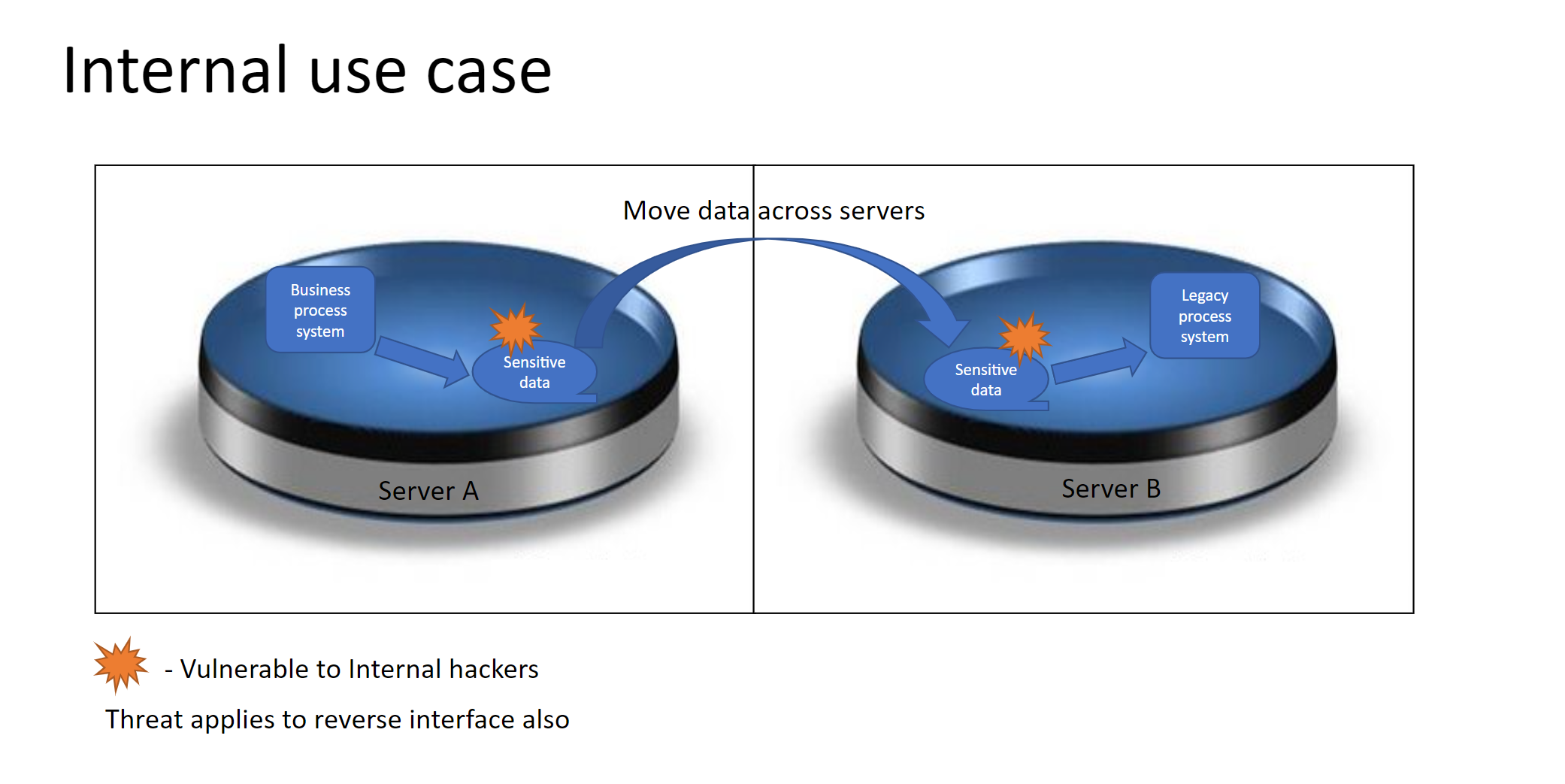
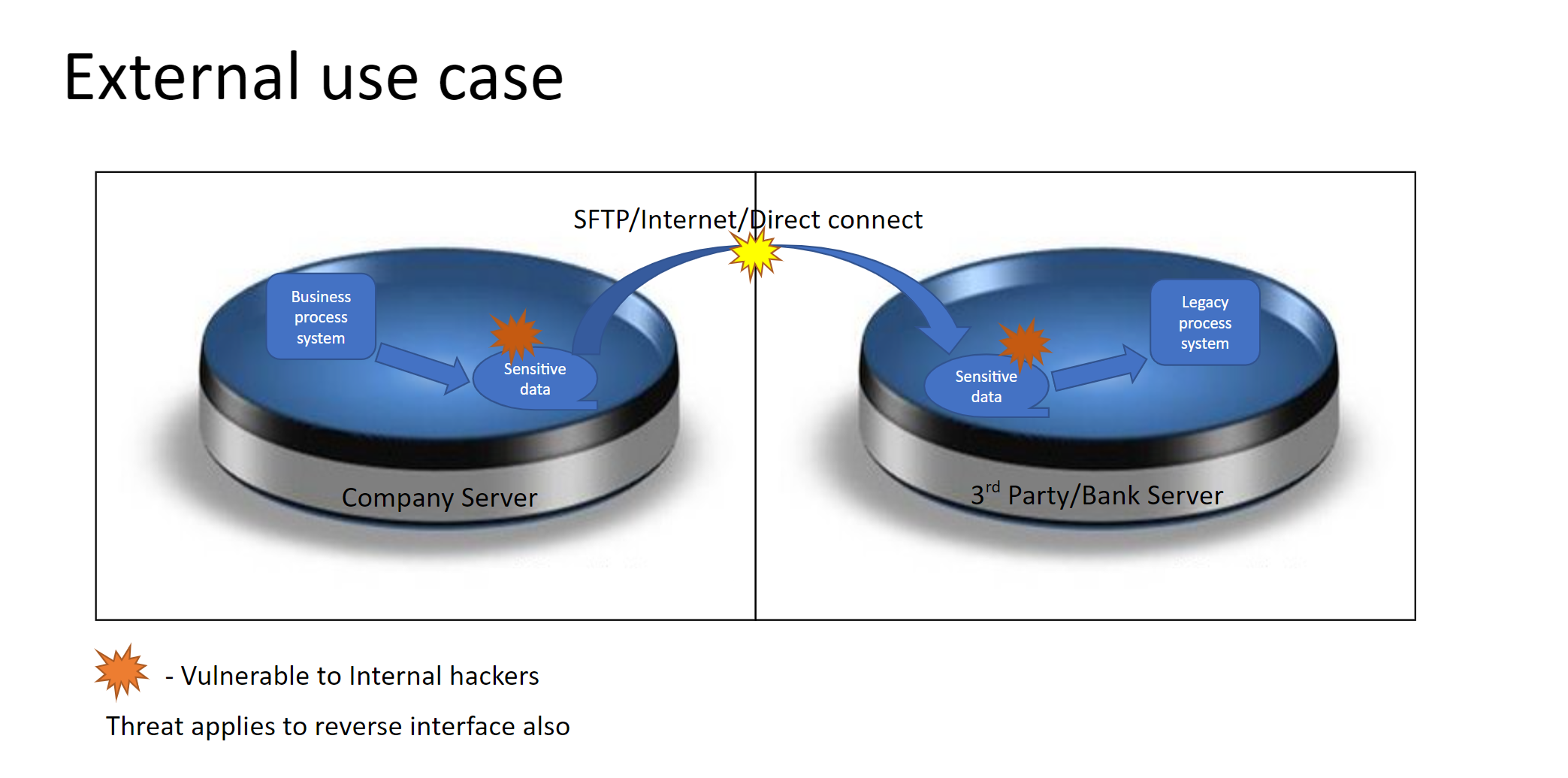
DAP tool is developed based on a real requirement to protect sensitive data from company internal and external vulnerable threat. Companies exchange sensitive data with bank account numbers, social security numbers between internal systems and external companies/Banks. In internal system interfaces, large volume of data is being downloaded from source system into local servers as files. Same file is moved to target system server for further processing. When the sensitive data file is sitting in source server and in target server until it is moved/consumed, the data is available for someone, who has access to the server files, to view and/or alter. Similar threat exists when sensitive data pushed through internet to external companies/Banks.
This tool protects data from both viewing and altering as:
- Encrypt to prevent sensitive data for someone to view
- Derive digital signature key and store in the same data file to validate at the target to validate any data alternation in-between systems.
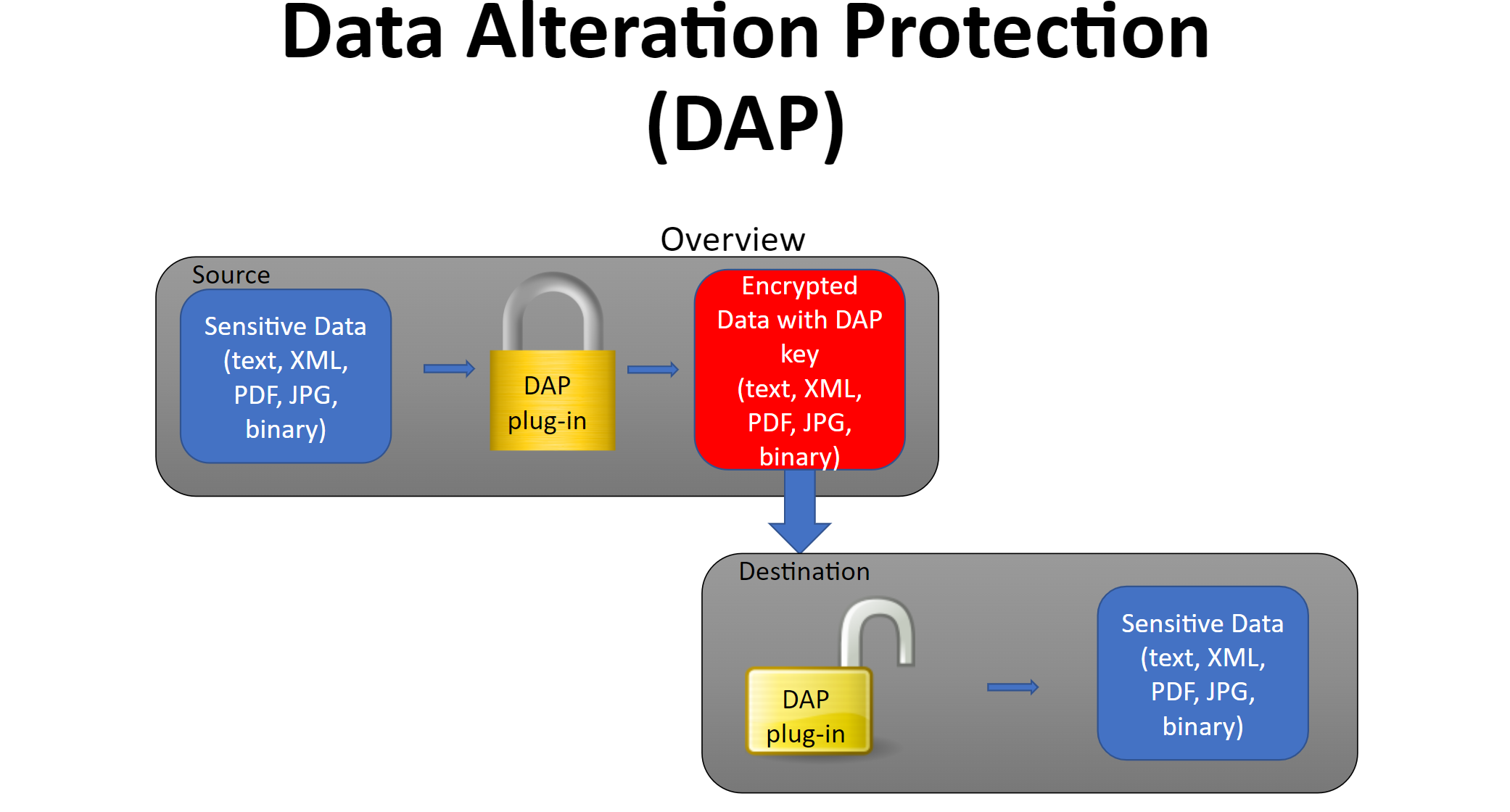
DAP function
- Visibility protection -Data encrypted using dynamic pattern change method
- Data tampering protection -Derives digital key at source data using its own algorithms
- In addition to algorithm, uses different levels of data restructuring
- Digital key is saved as part of data in a new file/memory at source
- At destination, data is decrypted, rederived digital key and compared against source key
- If no match, data from source become unusable
DAP highlights
- Developed in language ‘C’ for easy plug-in to any application
- Multi level digital key derivation for stronger protection
- Data encryption done using dynamically derived patterns
- Large data volume considered
- No change in existing data flow as DTP is a transparent plug-in
- No override option for digital key to avoid possible security breach
- Handles any file/data like .txt, .xml, .bin, .pdf, .tiff, etc.
- DAP tool to be installed at both source and destination systems
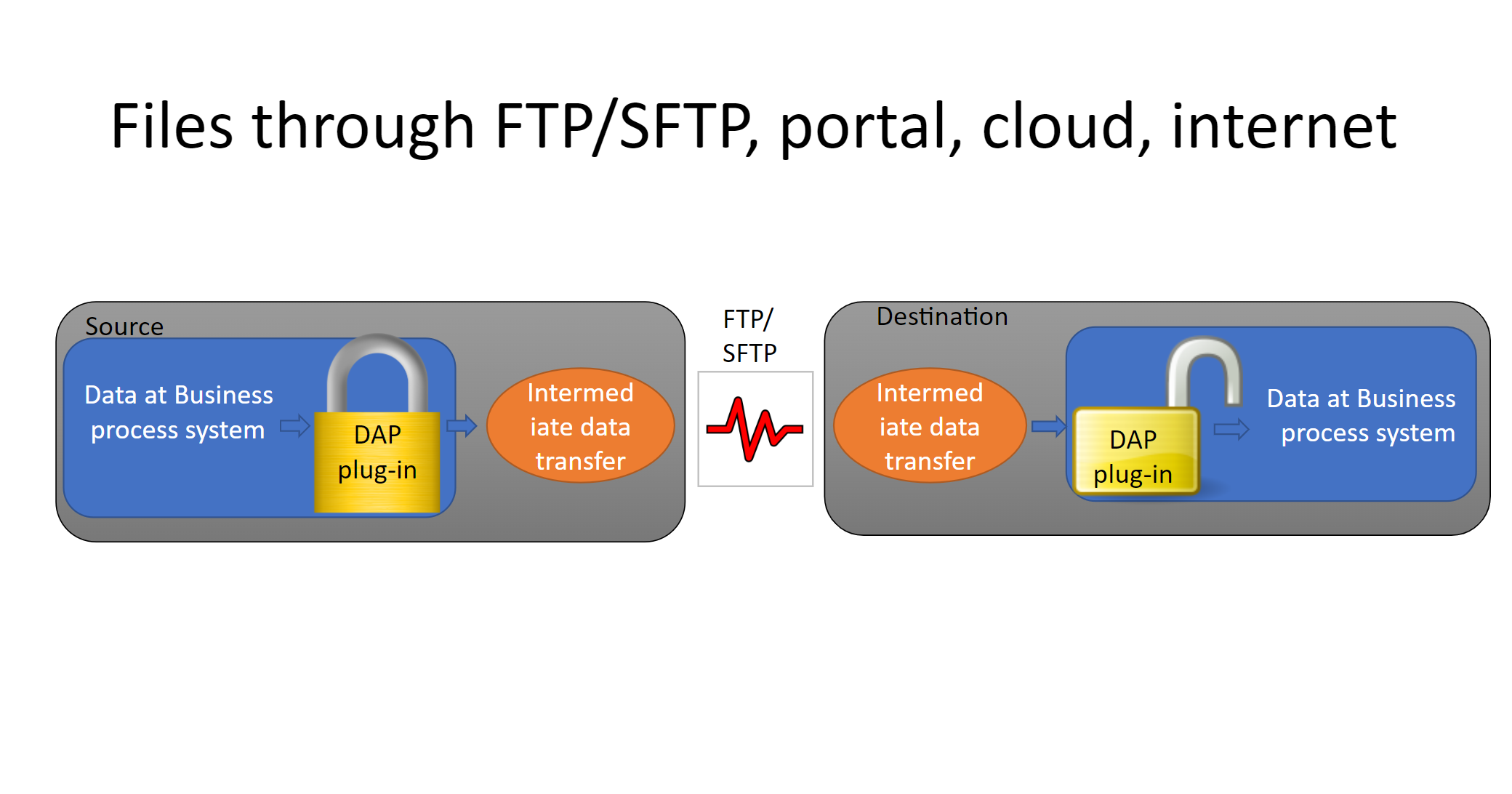
Data passing medium
- Files through FTP/SFTP
- Files through internet
- Data from memory to memory
- Text messages (may not be needed as already secured)
- Email recipient mail ids /subject /attachments /body (not needed as emails are 126 bits encrypted)
- Data between servers
- Data between process
- Data/files through cloud
- Data/files to portal